1. What is XGS-PON?
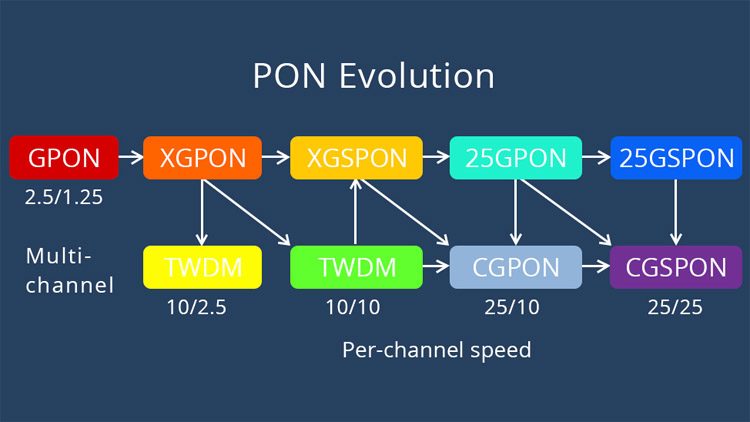
Both XG-PON and XGS-PON belong to the GPON series. From the technical roadmap, XGS-PON is the technological evolution of XG-PON.
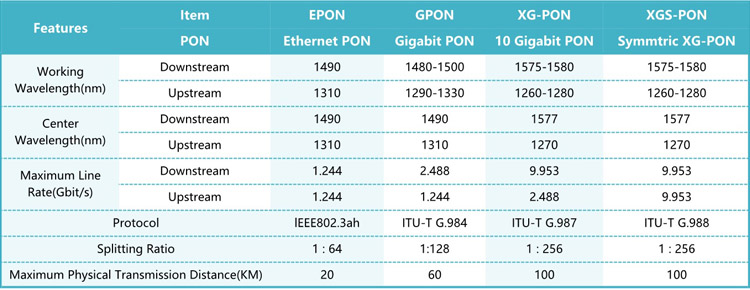
Both XG-PON and XGS-PON are 10G PON, the main difference is: XG-PON is an asymmetric PON, the uplink/downlink rate of the PON port is 2.5G/10G; XGS-PON is a symmetric PON, the uplink/downlink rate of the PON port The rate is 10G/10G.
The main PON technologies currently used are GPON and XG-PON, both of which are asymmetric PON. Since the user’s upstream/downlink data is generally asymmetrical, taking a certain first-tier city as an example, the average upstream traffic of the OLT is only 22% of the downstream traffic. Therefore, the technical characteristics of asymmetric PON are basically related to the needs of users. match. More importantly, the uplink rate of asymmetric PON is low, the cost of sending components such as lasers in ONU is low, and the equipment price is correspondingly low.
However, user needs are diverse. With the rise of live broadcasting and video surveillance services, there are more and more scenarios where users pay more attention to uplink bandwidth. Inbound dedicated lines need to provide symmetrical uplink/downlink circuits. These businesses promote the demand for XGS-PON.
2. Coexistence of XGS-PON, XG-PON and GPON
XGS-PON is the technological evolution of GPON and XG-PON, and supports mixed access of three types of ONUs: GPON, XG-PON and XGS-PON.
2.1 Coexistence of XGS-PON and XG-PON
Like XG-PON, the downlink of XGS-PON adopts the broadcast method, and the uplink adopts the TDMA method.
Since the downstream wavelength and downstream rate of XGS-PON and XG-PON are the same, the downstream of XGS-PON does not distinguish between XGS-PON ONU and XG-PON ONU, and the optical splitter broadcasts the downstream optical signal to the same ODN link For each XG(S)-PON (XG-PON and XGS-PON) ONU, each ONU chooses to receive its own signal and discards other signals.
The uplink of XGS-PON performs data transmission according to time slots, and ONU sends data in the time slots permitted by OLT. The OLT dynamically allocates time slots according to the traffic demands of different ONUs and the type of ONU (is it XG-PON or XGS-PON?). In the time slot allocated to XG-PON ONU, the data transmission rate is 2.5Gbps; in the time slot allocated to XGS-PON ONU, the data transmission rate is 10Gbps.
It can be seen that XGS-PON naturally supports mixed access with two types of ONUs, XG-PON and XGS-PON.
2.2 Coexistence of XGS-PON and GPON
Since the uplink/downlink wavelength is different from that of GPON, XGS-PON uses the Combo solution to share ODN with GPON. For the principle of the Combo solution, refer to the article “Discussion on the Solution to Improve the XG-PON Resource Utilization of the Combo Subscriber Board”.
The Combo optical module of XGS-PON integrates GPON optical module, XGS-PON optical module and WDM multiplexer.
In the upstream direction, after the optical signal enters the XGS-PON Combo port, WDM filters the GPON signal and XGS-PON signal according to the wavelength, and then sends the signal to different channels.
In the downlink direction, the signals from the GPON channel and the XGS-PON channel are multiplexed through WDM, and the mixed signal is downlinked to the ONU through the ODN. Since the wavelengths are different, different types of ONUs select the required wavelengths to receive signals through internal filters.
Since XGS-PON naturally supports coexistence with XG-PON, the Combo solution of XGS-PON supports the mixed access of GPON, XG-PON and XGS-PON three types of ONUs. The Combo optical module of XGS-PON is also called three Mode Combo optical module (XG-PON’s Combo optical module is called a two-mode Combo optical module because it supports the mixed access of GPON and XG-PON two types of ONUs).
3. Market Status
Affected by equipment cost and equipment maturity, the current equipment price of XGS-PON is much higher than that of XG-PON. Among them, the unit price of OLT (including Combo user board) is about 20% higher, and the unit price of ONU is more than 50% higher.
Although inbound dedicated lines need to provide uplink/downlink symmetrical circuits, the actual traffic of most inbound dedicated lines is still dominated by the following behavior. Although there are more and more scenarios where users pay more attention to uplink bandwidth, there is almost no case of services that cannot be accessed through XG-PON but must be accessed through XGS-PON.
Post time: Apr-12-2023