Based on years of research and development experience in Internet equipment, we discussed the technologies and solutions for home broadband indoor network quality assurance. First, it analyzes the current situation of home broadband indoor network quality, and summarizes various factors such as fiber optics, gateways, routers, Wi-Fi, and user operations that cause home broadband indoor network quality problems. Secondly, the new indoor network coverage technologies marked by Wi-Fi 6 and FTTR (Fiber To The Room) will be introduced.
1. Analysis of home broadband indoor network quality problems
In the process of FTTH(fiber-to-home), due to the influence of optical transmission distance, optical splitting and connection device loss, and optical fiber bending, the optical power received by the gateway may be low and the bit error rate may be high, resulting in an increase in the packet loss rate of upper-layer service transmission. , the rate drops.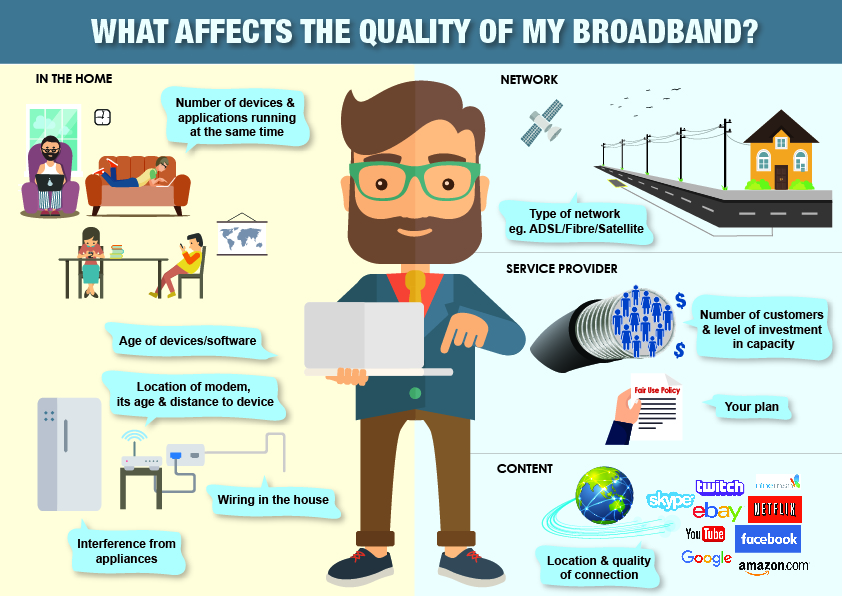
However, the hardware performance of old gateways is generally low, and problems such as high CPU and memory usage and overheating of equipment are prone to occur, resulting in abnormal restarts and crashes of gateways. Old gateways generally do not support gigabit network speeds, and some old gateways also have problems such as outdated chips, which lead to a large gap between the actual speed value of the network connection and the theoretical value, which further limits the possibility of improving the user’s online experience. At present, the old smart home gateways that have been used for 3 years or more on the live network still occupy a certain proportion and need to be replaced.
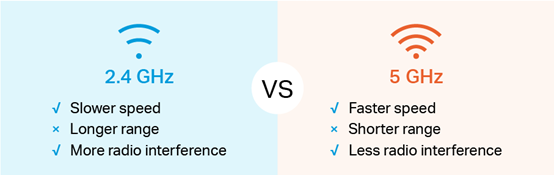
The 2.4GHz frequency band is the ISM (Industrial-Scientific-Medical) frequency band. It is used as a common frequency band for radio stations such as wireless local area network, wireless access system, Bluetooth system, point-to-point or point-to-multipoint spread spectrum communication system, with few frequency resources and limited bandwidth. At present, there are still a certain proportion of gateways supporting the 2.4GHz Wi-Fi frequency band in the existing network, and the problem of co-frequency/adjacent frequency interference is more prominent.
Due to software bugs and insufficient hardware performance of some gateways, PPPoE connections are frequently dropped and gateways are frequently restarted, resulting in frequent interruption of Internet access for users. After the PPPoE connection is passively interrupted (for example, the uplink transmission link is interrupted), each gateway manufacturer has inconsistent implementation standards for WAN port detection and re-performing PPPoE dialing. Some manufacturers’ gateways detect once every 20 seconds, and redial only after 30 failed detections. As a result, it takes 10 minutes for the gateway to automatically initiate PPPoE replay after passively going offline, seriously affecting user experience.
More and more users’ home gateways are configured with routers (hereinafter referred to as “routers”). Among these routers, quite a few only support 100M WAN ports, or (and) only support Wi-Fi 4 (802.11b/g/n).
Some manufacturers’ routers still have only one of the WAN ports or Wi-Fi protocols that supports Gigabit network speeds, and become “pseudo-Gigabit” routers. In addition, the router is connected to the gateway through a network cable, and the network cable used by users is basically a category 5 or super category 5 cable, which has a short life and weak anti-interference ability, and most of them only support 100M speed. None of the above-mentioned routers and network cables can meet the evolution requirements of subsequent gigabit and super-gigabit networks. Some routers restart frequently due to product quality problems, seriously affecting user experience.
Wi-Fi is the main indoor wireless coverage method, but many home gateways are placed in weak current boxes at the user’s door. Limited by the location of the weak current box, the material of the cover, and the complicated house type, the Wi-Fi signal is not enough to cover all indoor areas. The farther the terminal device is from the Wi-Fi access point, the more obstacles there are, and the greater the loss of signal strength, which may lead to unstable connection and data packet loss.
In the case of indoor networking of multiple Wi-Fi devices, the same-frequency and adjacent-channel interference problems often occur due to unreasonable channel settings, further reducing the Wi-Fi rate.
When some users connect the router to the gateway, due to lack of professional experience, they may connect the router to the non-gigabit network port of the gateway, or they may not connect the network cable tightly, resulting in loose network ports. In these cases, even if the user subscribes to the gigabit service or uses a gigabit router, he cannot obtain stable gigabit services, which also brings challenges for operators to deal with faults.
Some users have too many devices connected to Wi-Fi in their homes (more than 20) or multiple applications download files at high speed at the same time, which will also cause serious Wi-Fi channel conflicts and unstable Wi-Fi connections.
Some users use old terminals that only support single-frequency Wi-Fi 2.4GHz frequency band or older Wi-Fi protocols, so they cannot obtain a stable and fast Internet experience.
2. New technologies to improve indoor network Quality
High-bandwidth, low-latency services such as 4K/8K high-definition video, AR/VR, online education, and home office are gradually becoming the rigid needs of home users. This puts forward higher requirements on the quality of the home broadband network, especially the quality of the home broadband indoor network. The existing home broadband indoor network based on FTTH (Fiber To The House, fiber to the home) technology has been difficult to meet the above requirements. However, Wi-Fi 6 and FTTR technologies can better meet the above service requirements and should be deployed on a large scale as soon as possible.
Wi-Fi 6
In 2019, the Wi-Fi Alliance named the 802.11ax technology Wi-Fi 6, and named the previous 802.11ax and 802.11n technologies Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 4 respectively.
Wi-Fi 6 introduces OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access, Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access), MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple-Input Multiple-Output, multi-user multiple-input multiple-output technology), 1024QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation , quadrature amplitude modulation) and other new technologies, the theoretical maximum download rate can reach 9.6Gbit/s. Compared with the most widely used Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 5 technologies in the industry, it has higher transmission rate, greater concurrency capability, lower service delay, wider coverage and smaller terminal power. consumption.
FTTR Technology
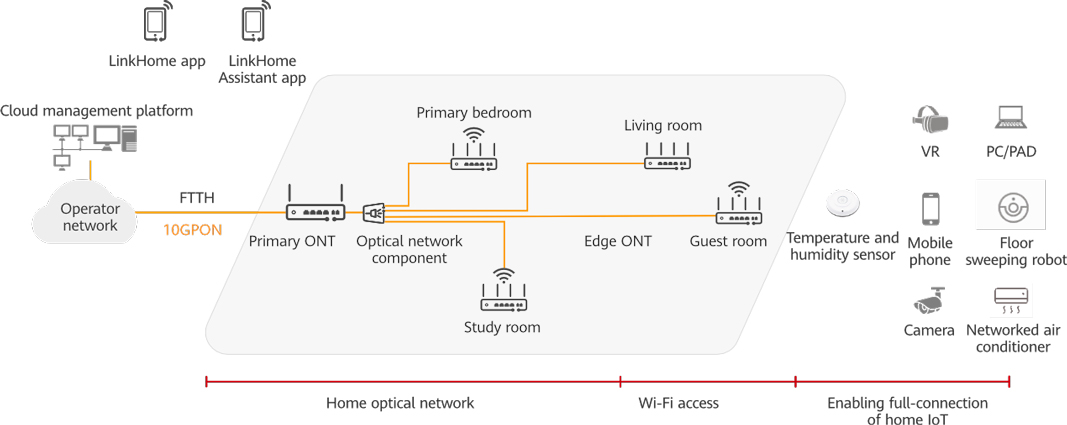
FTTR refers to the deployment of all-optical gateways and sub-devices in homes on the basis of FTTH, and the realization of optical fiber communication coverage to user rooms through PON technology.
The FTTR main gateway is the core of the FTTR network. It is connected upward to the OLT to provide fiber-to-the-home, and downward to provide optical ports to connect multiple FTTR slave gateways. The FTTR slave gateway communicates with the terminal equipment through Wi-Fi and Ethernet interfaces, provides a bridging function to forward the data of the terminal equipment to the main gateway, and accepts the management and control of the FTTR main gateway. The FTTR networking is shown in the figure.
Compared with traditional methods such as network cable networking, power line networking, and wireless networking, FTTR networks have the following advantages.
First, the networking equipment has better performance and higher bandwidth. The optical fiber connection between the master gateway and the slave gateway can really extend the gigabit bandwidth to every room of the user, and improve the quality of the user’s home network in all aspects. The FTTR network has more advantages in transmission bandwidth and stability.
The second is better Wi-Fi coverage and higher quality. Wi-Fi 6 is the standard configuration of FTTR gateways, and both the master gateway and the slave gateway can provide Wi-Fi connections, effectively improving the stability of Wi-Fi networking and signal coverage strength.
The quality of the home network intranet is affected by factors such as the home network layout, user equipment, and user terminals. Therefore, finding and locating the poor quality of the home network is a difficult problem on the live network. Each communication company or network service provider puts forward its own solution respectively. For example, technical solutions for evaluating the quality of the home network intranet and locating poor quality; continue to explore the application of big data and artificial intelligence technology in the field of improving the quality of home broadband indoor networks; promote the application of FTTR and Wi-Fi 6 technology Wide network quality base and more.
Post time: May-08-2023