WiFi 7 (Wi-Fi 7) is the next-generation Wi-Fi standard. Corresponding to IEEE 802.11, a new revised standard IEEE 802.11be – Extremely High Throughput (EHT) will be released
Wi-Fi 7 introduces technologies such as 320MHz bandwidth, 4096-QAM, Multi-RU, multi-link operation, enhanced MU-MIMO, and multi-AP cooperation on the basis of Wi-Fi 6, making Wi-Fi 7 more powerful than Wi-Fi 7. Because Wi-Fi 6 will provide higher data transfer rates and lower latency. Wi-Fi 7 is expected to support a throughput of up to 30Gbps, about three times that of Wi-Fi 6.
New Features Supported by Wi-Fi 7
- Support maximum 320MHz bandwidth
- Support Multi-RU mechanism
- Introduce higher order 4096-QAM modulation technology
- Introduce Multi-Link multi-link mechanism
- Support more data streams, MIMO function enhancement
- Support cooperative scheduling among multiple APs
- Application Scenarios of Wi-Fi 7
1. Why Wi-Fi 7?
With the development of WLAN technology, families and enterprises rely more and more on Wi-Fi as the main means of accessing the network. In recent years, new applications have higher throughput and delay requirements, such as 4K and 8K video (the transmission rate may reach 20Gbps), VR/AR, games (the delay requirement is less than 5ms), remote office, and online video conferencing and cloud computing, etc. Although the latest release of Wi-Fi 6 has focused on user experience in high-density scenarios, it still cannot fully meet the above-mentioned higher requirements for throughput and latency. (Welcome to pay attention to the official account: network engineer Aaron)
To this end, the IEEE 802.11 standard organization is about to release a new revised standard IEEE 802.11be EHT, namely Wi-Fi 7.
2. Release time of Wi-Fi 7
The IEEE 802.11be EHT working group was established in May 2019, and the development of 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) is still in progress. The entire protocol standard will be released in two Releases, and Release1 is expected to release the first version in 2021 Draft Draft1.0 is expected to release the standard by the end of 2022; Release2 is expected to start in early 2022 and complete the standard release by the end of 2024.
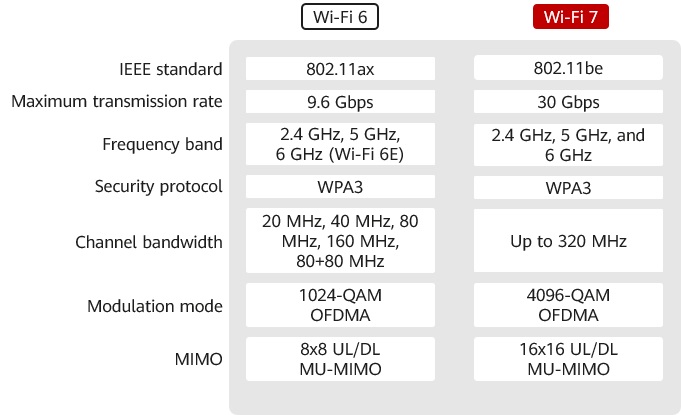
3. Wi-Fi 7 vs Wi-Fi 6
Based on the Wi-Fi 6 standard, Wi-Fi 7 introduces many new technologies, mainly reflected in:
4. New Features Supported by Wi-Fi 7
The goal of the Wi-Fi 7 protocol is to increase the throughput rate of the WLAN network to 30Gbps and provide low-latency access guarantees. In order to meet this goal, the entire protocol has made corresponding changes in the PHY layer and MAC layer. Compared with the Wi-Fi 6 protocol, the main technical changes brought about by the Wi-Fi 7 protocol are as follows:
Support Maximum 320MHz Bandwidth
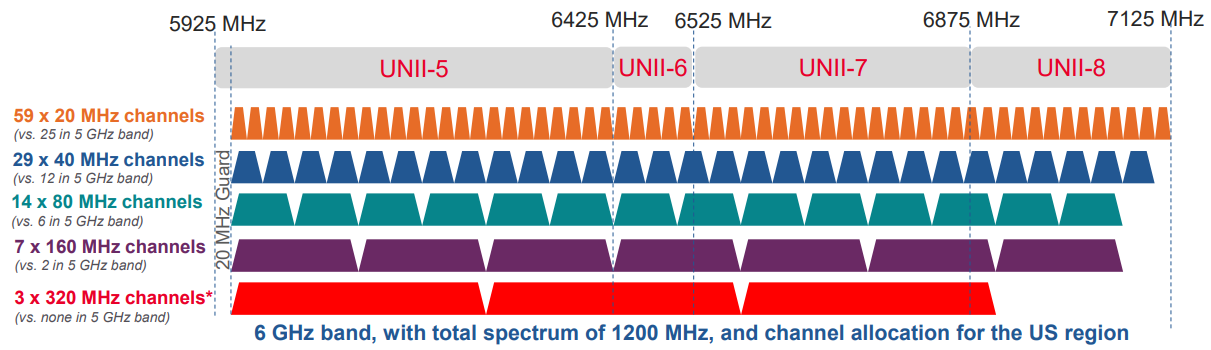
The license-free spectrum in the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands is limited and crowded. When existing Wi-Fi runs emerging applications such as VR/AR, it will inevitably encounter the problem of low QoS. In order to achieve the goal of a maximum throughput of no less than 30Gbps, Wi-Fi 7 will continue to introduce the 6GHz frequency band and add new bandwidth modes, including continuous 240MHz, non-continuous 160+80MHz, continuous 320 MHz and non-continuous 160+160MHz. (Welcome to pay attention to the official account: network engineer Aaron)
Support Multi-RU Mechanism
In Wi-Fi 6, each user can only send or receive frames on the assigned specific RU, which greatly limits the flexibility of spectrum resource scheduling. To solve this problem and further improve spectrum efficiency, Wi-Fi 7 defines a mechanism that allows multiple RUs to be allocated to a single user. Of course, in order to balance the complexity of the implementation and the utilization of the spectrum, the protocol has made certain restrictions on the combination of RUs, that is: small-sized RUs (RUs smaller than 242-Tone) can only be combined with small-sized RUs, and large-sized RUs (RUs greater than or equal to 242-Tone) can only be combined with large-sized RUs, and small-sized RUs and large-sized RUs are not allowed to be mixed.
Introduce higher order 4096-QAM modulation technology
The highest modulation method of Wi-Fi 6 is 1024-QAM, in which the modulation symbols carry 10 bits. In order to further increase the rate, Wi-Fi 7 will introduce 4096-QAM, so that the modulation symbols carry 12 bits. Under the same encoding, Wi-Fi 7′s 4096-QAM can achieve a 20% rate increase compared to Wi-Fi 6′s 1024-QAM. (Welcome to pay attention to the official account: network engineer Aaron)
Introduce Multi-Link multi-link mechanism
In order to achieve efficient utilization of all available spectrum resources, there is an urgent need to establish new spectrum management, coordination and transmission mechanisms on 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz. The working group defined technologies related to multi-link aggregation, mainly including MAC architecture of enhanced multi-link aggregation, multi-link channel access, multi-link transmission and other related technologies.
Support more data streams, MIMO function enhancement
In Wi-Fi 7, the number of spatial streams has increased from 8 to 16 in Wi-Fi 6, which theoretically can more than double the physical transmission rate. Supporting more data streams will also bring more powerful features-distributed MIMO, which means that 16 data streams can be provided not by one access point, but by multiple access points at the same time, which means multiple APs need to cooperate with each other to work.
Support cooperative scheduling among multiple APs
Currently, within the framework of the 802.11 protocol, there is actually not much cooperation between APs. Common WLAN functions such as automatic tuning and smart roaming are vendor-defined features. The purpose of inter-AP cooperation is only to optimize channel selection, adjust the load among APs, etc., so as to achieve the purpose of efficient utilization and balanced allocation of radio frequency resources. Coordinated scheduling between multiple APs in Wi-Fi 7, including coordinated planning between cells in the time domain and frequency domain, interference coordination between cells, and distributed MIMO, can effectively reduce interference between APs, greatly Improve the utilization of air interface resources.

There are many ways to coordinate scheduling between multiple APs, including C-OFDMA (Coordinated Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access), CSR (Coordinated Spatial Reuse), CBF (Coordinated Beamforming), and JXT (Joint Transmission).
5. Application Scenarios of Wi-Fi 7
The new features introduced by Wi-Fi 7 will greatly increase the data transmission rate and provide lower latency, and these advantages will be more helpful to emerging applications, as follows:
- Video stream
- Video/Voice Conferencing
- Wireless gaming
- Real-time collaboration
- Cloud/Edge Computing
- Industrial Internet of Things
- Immersive AR/VR
- interactive telemedicine
Post time: Feb-20-2023