The core goal of building a “gigabit city” is to build a foundation for the development of the digital economy and promote the social economy into a new stage of high-quality development. For this reason, the author analyzes the development value of “gigabit cities” from the perspectives of supply and demand.
On the supply side, “gigabit cities” can maximize the effectiveness of digital “new infrastructure”.
Over the past few decades, it has been proved by practice to use large-scale infrastructure investment to stimulate the growth of related industries and build a good foundation for the sustainable development of the social economy. As new energy and new information and communication technologies gradually become the leading driving force for social and economic development, it is necessary to further strengthen the construction of new infrastructure to achieve “shifting” development.
First of all, digital technologies such as Gigabit Passive Optic Networks have a significant return on leverage. According to an analysis by Oxford Economics, for every $1 increase in digital technology investment, GDP can be leveraged to increase by $20, and the average rate of return on investment in digital technology is 6.7 times that of non-digital technology.
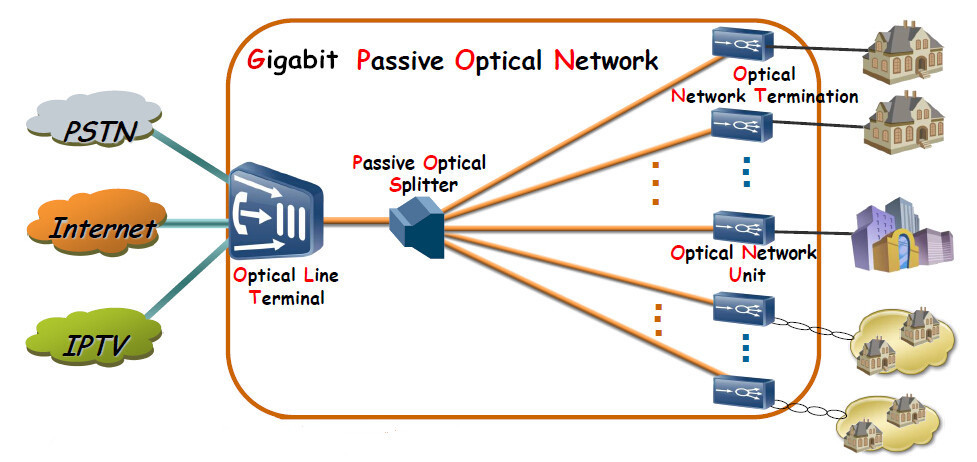
Secondly, the Gigabit Passive Optic Network construction relies on a large-scale industrial system, and the linkage effect is obvious. The so-called gigabit does not mean that the peak rate of the terminal connection side reaches gigabit, but that it needs to ensure the stable use experience of the Gigabit Passive Optic Network and promote the green and energy-saving development of the industry. As a result, (GPON)Gigabit Passive Optic Networks have promoted the design and construction of new network architectures, such as cloud-network integration, “East Data, West Computing” and other models, which have promoted the expansion of backbone networks and the construction of data centers, computing power centers, and edge computing facilities. , Promote innovation in various fields in the information and communication industry, including chip modules, 5G and F5G standards, green energy-saving algorithms, etc.
Finally, “gigabit city” is the most effective way to promote the implementation of Gigabit Passive Optic Network construction. One is that urban population and industries are dense, and with the same resource input, it can achieve wider coverage and deeper applications than rural areas; second, telecom operators are more active in investing in urban infrastructure that can quickly earn returns. As a profit center, it adopts the method of “construction-operation-profit” to promote, while for infrastructure construction in rural areas, it focuses more on the realization of universal services; third, cities (especially central cities) have always been new In areas where technologies, new products, and new facilities are first implemented, the construction of “gigabit cities” will play a demonstration role and promote the popularization of Gigabit Passive Optic Networks.
On the demand side, “gigabit cities” can empower the leveraged development of the digital economy.
It is already an axiom that infrastructure construction can play a leverage role in promoting social and economic development. As for the question of “the chicken or the egg first”, looking back at the development of the industrial economy, it is generally technology-first, and then pilot products or solutions appear; large-scale construction of infrastructure, the formation of sufficient momentum for the entire industry, through innovation, Marketing and promotion, industrial cooperation and other methods allow the leveraged investment value of infrastructure to be effectively realized.
The Gigabit Passive Optic Network construction represented by “gigabit city” is no exception. When the police began to promote the construction of a “dual gigabit” network, it was artificial intelligence, blockchain, metaverse, ultra-high-definition video, etc. The eve of the full-scale rise of emerging information and communication technologies represented by the Internet of Things coincides with the start of the comprehensive digitalization of the industry.
The construction of a Gigabit Passive Optic Network, not only makes a qualitative leap in the existing user experience (such as watching videos, playing games, etc.) but also clears the way for the development of new industries and new applications. For example, the live broadcast industry is developing towards the direction of live broadcast for everyone, and high-definition, low-latency, and interactive capabilities have become a reality; the medical industry has realized the comprehensive popularization of telemedicine.
In addition, the development of Gigabit Passive Optic Networks will also help energy conservation and emission reduction, and help the early realization of the “double carbon” goal. On the one hand, Gigabit Passive Optic Network construction is a process of upgrading information infrastructure, realizing the “shift” too low energy consumption; on the other hand, through digital transformation, the operational efficiency of various assets has been improved. For example, according to estimates, only in In terms of construction and application of F5G, it can help reduce 200 million tons of carbon dioxide emissions in the next 10 years.
Post time: Feb-27-2023