1. Overview
Wireless AP (Wireless Access Point), that is, wireless access point, is used as a wireless switch of a wireless network and is the core of a wireless network. Wireless AP is the access point for wireless devices (such as portable computers, mobile terminals, etc.) to enter the wired network. It is mainly used in broadband homes, buildings and parks, and can cover tens of meters to hundreds of meters.
Wireless AP is a name with a wide range of meanings. It not only includes simple wireless access points (Wireless APs), but also a general term for wireless routers (including wireless gateways, wireless bridges) and other devices.
Wireless AP is a typical application of wireless local area network. Wireless AP is a bridge connecting wireless network and wired network, and it is the core equipment for establishing wireless local area network (WLAN). It provides the function of mutual access between wireless devices and wired LANs. With the help of wireless APs, wireless devices within the signal coverage of wireless APs can communicate with each other. Without wireless APs, it is basically impossible to build a real WLAN that can access the Internet. . The wireless AP in the WLAN is equivalent to the role of the transmitting base station in the mobile communication network.
Compared with the wired network architecture, the wireless AP in the wireless network is equivalent to the hub in the wired network. It can connect various wireless devices. The network card used by the wireless device is a wireless network card, and the transmission medium is air (electromagnetic wave). Wireless AP is the central point of a wireless unit, and all wireless signals in the unit must pass through it for exchange.
2. Functions
2.1 Connect wireless and wired
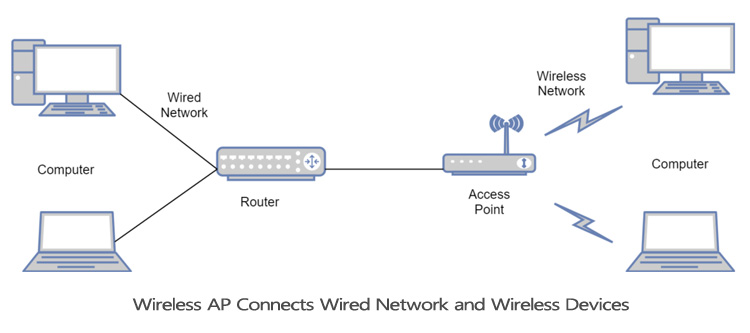
The most common function of the wireless AP is to connect the wireless network and the wired network, and provide the function of mutual access between the wireless device and the wired network. As shown in Figure 2.1-1.
Wireless AP connects wired network and wireless devices
2.2 WDS
WDS (Wireless Distribution System), that is, wireless hotspot distribution system, it is a special function in wireless AP and wireless router. It is a very practical function to realize the communication between two wireless devices. For example, there are three neighbors, and each household has a wireless router or wireless AP that supports WDS, so that the wireless signal can be covered by the three households at the same time, making mutual communication more convenient. However, it should be noted that the WDS devices supported by the wireless router are limited (Generally 4-8 devices can be supported), and WDS devices of different brands may also fail to connect.
2.3 Functions of wireless AP
2.3.1 Relay
An important function of wireless AP is relay. The so-called relay is to amplify the wireless signal once between two wireless points, so that the remote wireless device can receive a stronger wireless signal. For example, an AP is placed at point a, and there is a wireless device at point c. There is a distance of 120 meters between point a and point c. The wireless signal transmission from point a to point c has been weakened a lot, so it can be 60 meters away. Place a wireless AP as a relay at point b, so that the wireless signal at point c can be effectively enhanced, thus ensuring the transmission speed and stability of the wireless signal.
2.3.2 Bridging
An important function of wireless AP is bridging. Bridging is to connect two wireless AP endpoints to realize data transmission between two wireless APs. In some scenarios, if you want to connect two wired LANs, you can choose to bridge through a wireless AP. For example, at point a there is a wired LAN composed of 15 computers, and at point b there is a wired LAN composed of 25 computers, but the distance between points ab and ab is very far, exceeding 100 meters, so it is not suitable to connect by cable. At this time, you can set up a wireless AP at point a and point b respectively, and turn on the bridging function of the wireless AP, so that the LANs at points ab and ab can transmit data to each other.
2.3.3 Master-slave mode
Another function of wireless AP is “master-slave mode”. The wireless AP working in this mode will be regarded as a wireless client (such as wireless network card or wireless module) by the master wireless AP or wireless router. It is convenient for the network management to manage the sub-network and realize a point-to-multipoint connection (the wireless router or the main wireless AP is one point, and the client of the wireless AP is multi-point). The “master-slave mode” function is often used in the connection scenarios of wireless LAN and wired LAN. For example, point a is a wired LAN composed of 20 computers, and point b is a wireless LAN composed of 15 computers. Point b is already There is a wireless router. If point a wants to access point b, you can add a wireless AP at point a, connect the wireless AP to the switch at point a, and then turn on the “master-slave mode” of the wireless AP and the wireless connection at point b. The router is connected, and at this time all the computers at point a can connect to the computers at point b.
3. Differences between Wireless AP and Wireless Router
3.1 Wireless AP
Wireless AP, that is, wireless access point, is simply a wireless switch in a wireless network. It is an access point for mobile terminal users to enter a wired network. It is mainly used for home broadband and enterprise internal network deployment. The wireless coverage distance is Tens of meters to hundreds of meters, the main technology is 802.11X series. General wireless APs also have an access point client mode, which means that wireless links can be performed between APs, thereby expanding the coverage of the wireless network.
Since the simple wireless AP lacks the routing function, it is equivalent to a wireless switch and only provides a function of wireless signal transmission. Its working principle is to receive the network signal transmitted by the twisted pair, and after compiling by the wireless AP, convert the electrical signal into a radio signal and send it out to form the coverage of the wireless network.
3.2 Wireless Router
The extended wireless AP is what we often call a wireless router. A wireless router, as its name implies, is a router with a wireless coverage function, which is mainly used for users to surf the Internet and wireless coverage. Compared with the simple wireless AP, the wireless router can realize the Internet connection sharing in the home wireless network through the routing function, and can also realize the wireless shared access of ADSL and community broadband.
It is worth mentioning that wireless and wired terminals can be assigned to a subnet through a wireless router, so that various devices in the subnet can exchange data conveniently.
3.3 Summary
In a brief summary, the simple wireless AP is equivalent to a wireless switch; the wireless router (extended wireless AP) is equivalent to “wireless AP + router function”. In terms of usage scenarios, if the home is already connected to the Internet and just want to provide wireless access, then choosing a wireless AP is enough; but if the home is not yet connected to the Internet, we need to connect to the Internet Wireless access function, then you need to choose a wireless router at this time.
In addition, from the appearance point of view, the two are basically similar in length, and it is not easy to distinguish them. However, if you look closely, you can still see the difference between the two: that is, their interfaces are different. (Simple type) wireless AP usually has a wired RJ45 network port, a power supply port, a configuration port (USB port or configuration through the WEB interface), and fewer indicator lights; while a wireless router has four more wired network ports, except One WAN port is used to connect to the upper-level network equipment, and the four LAN ports can be wired to connect to computers in the intranet, and there are more indicator lights.
Post time: Apr-19-2023